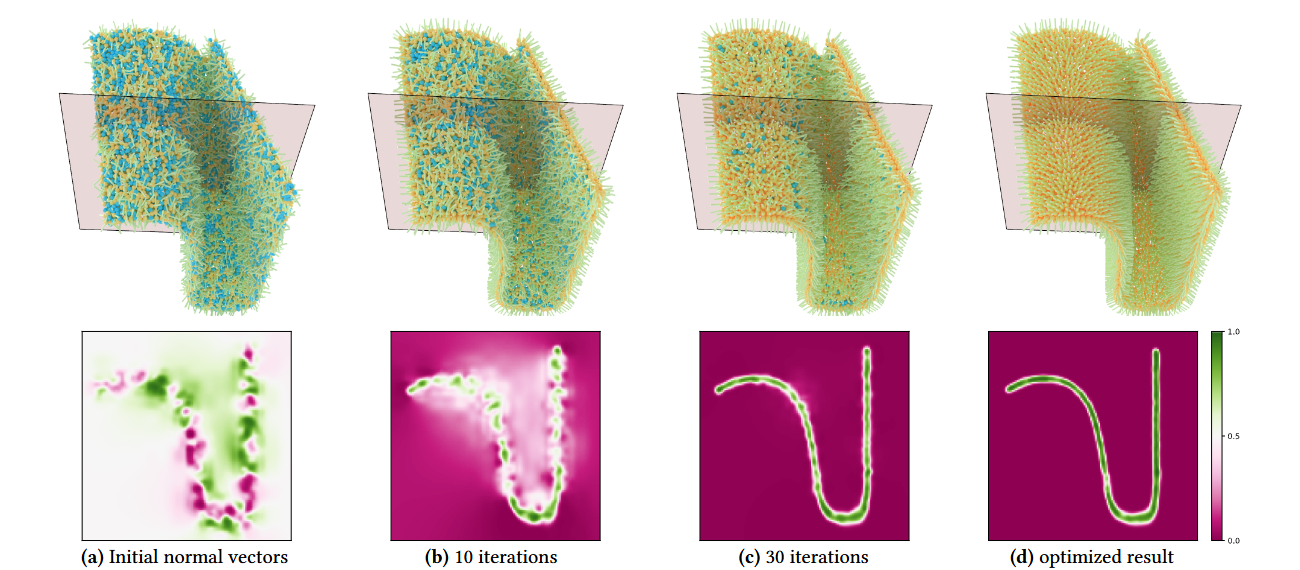
Figure 1: Starting from a set of completely random normals (a), we repeatedly optimize their directions (b,c) until convergence (d).
Abstract
We propose a simple yet effective method to orient normals for point clouds. Central to our approach is a novel optimization objective function defined from global and local perspectives. Globally, we introduce a signed uncertainty function that distinguishes the inside and outside of the underlying surface. Moreover, benefiting from the statistics of our global term, we present a local orientation term instead of a global one. The optimization problem can be solved by the commonly used numerical optimization solver, such as L-BFGS. The capability and feasibility of our approach are demonstrated over various complex point clouds. We achieve higher practical robustness and normal quality than the state-of-the-art methods.
Normal orientation, Gaussian processes, Surface reconstruction
Reconstructing surfaces from point clouds is a challenging task. Since point clouds themselves do not define a surface and there are infinitely many surfaces that can approximate a given point cloud, this is an ill-posed problem. Therefore, adding additional assumptions and constraints is crucial. Consistent directional normals provide both the surface orientation and local geometric information at each point. We propose a simple and effective method for determining the normals of point clouds. The core of our method is to combine global and local information to define a new optimization objective function: globally, we introduce a signed uncertainty function to distinguish between the interior and exterior of the surface; leveraging the statistical uncertainty information from the global term, the directional estimation can be replaced with local estimates.
The method proposed in this paper involves optimizing a stochastic probability model where the variables are the distributions of point normals. By leveraging the SRSR probability model, we observe that if the normals are accurate and reliable, the probability of a point being inside the shape approaches 1 when the point is inside the surface and approaches 0 when the point is outside the surface. Conversely, if the normals are random or inconsistent, the probability tends to approach 0.5.
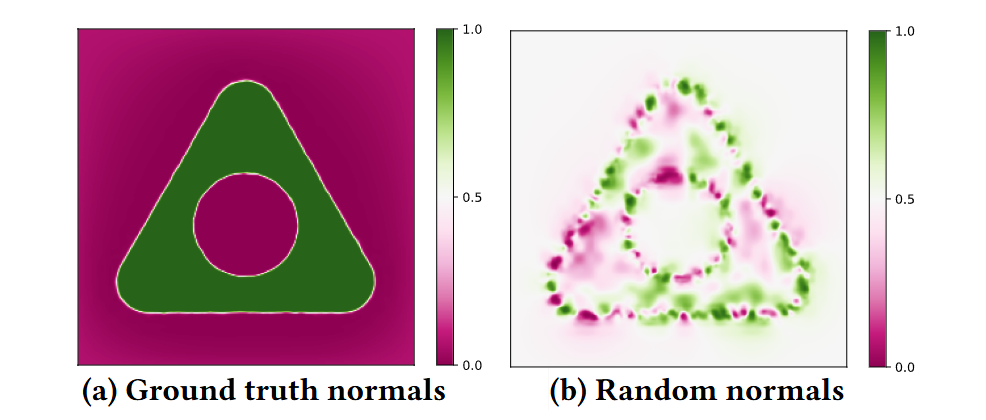
Figure 2: The probability that the point in space belongs to the interior of the surface tends to 1 or 0 if the normals are correct (a). The probability that the point in space far from point clouds belongs to the interior of the surface is close to 0.5 if the normals are random (b).
This probability distribution can be used to measure spatial uncertainty and quantify the quality of normals, allowing us to define an uncertainty function for optimizing normal quality. However, the uncertainty function defined solely by the probability distribution lacks directional guidance. To address this, we introduce a local directional term, which yields a positive value outside the surface and a negative value inside the surface when the normals are correct and reliable, thereby creating a signed uncertainty function. By using L-BFGS to optimize this signed uncertainty function, we obtain consistent normal directions.
Code
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions and comments. This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62272429, 62025207) and Xiaomi Foundation. Xiao-Ming Fu is a USTC Tang Scholar.
@article {huang2024reconstruction,
title = {Stochastic Normal Orientation for Point Clouds},
author = {Huang, Guojin and Fang, Qing and Zhang, Zheng and Liu, Ligang and Fu, Xiao-Ming}
journal = {ACM Transactions on Graphics},
volume={43},
number={6},
pages={1--11},
year = {2024}
}